-
-
-
Tổng tiền thanh toán:
-
Thermal power plant: benefits, advantages, disadvantages and solutions?
CÔNG TY CỔ PHẦN THIẾT BỊ VẬT TƯ MINH HẢI
09/10/2023
0 nhận xét
Thermal power plants are electricity generation facilities that use heat energy to produce electrical power. They operate by converting thermal energy, typically derived from the combustion of fossil fuels or nuclear reactions, into mechanical energy and then into electrical energy through a generator. While they have played a significant role in meeting global energy demands, they come with a set of benefits, advantages, disadvantages, and associated solutions.
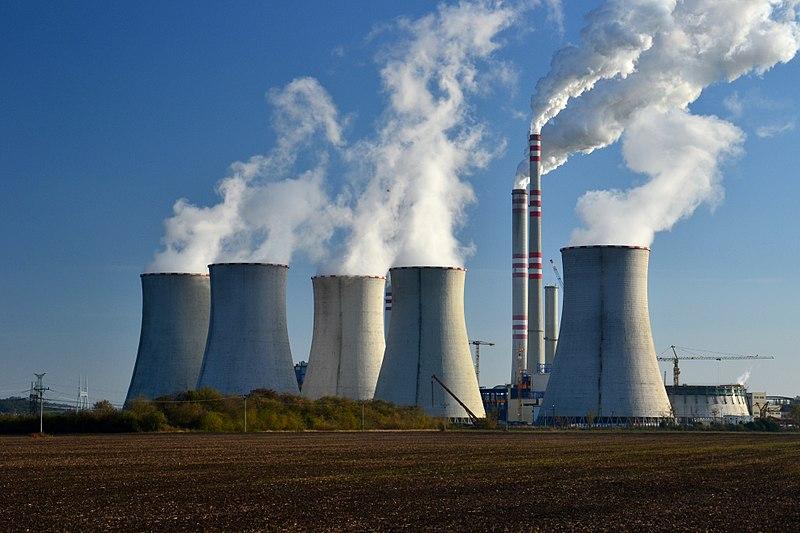
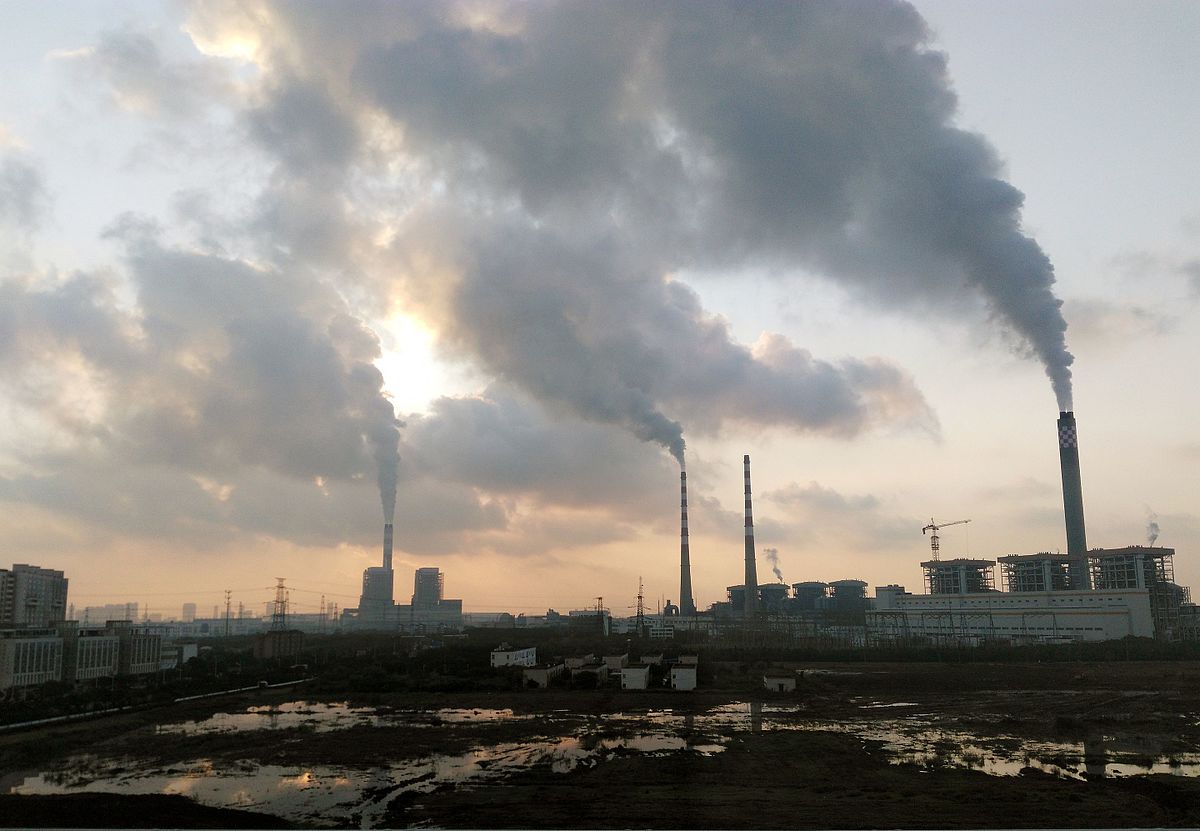


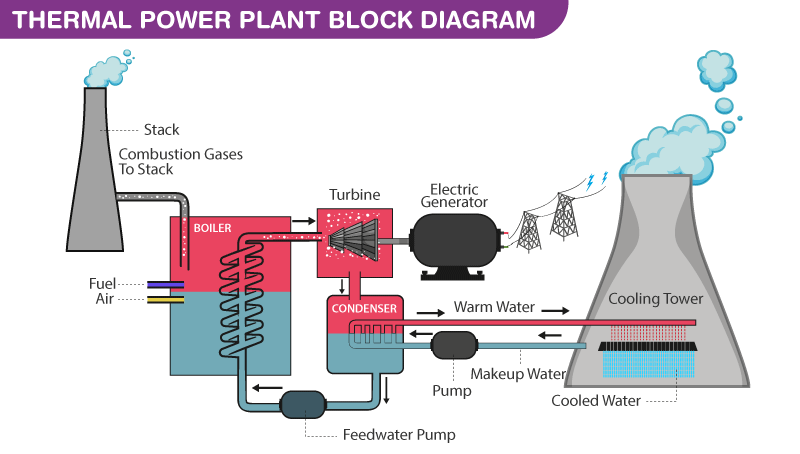
Benefits and Advantages of Thermal Power Plants:
-
Reliability: Thermal power plants are known for their reliability and can provide a steady supply of electricity, making them suitable for baseload power generation.
-
Efficiency: Modern thermal power plants are highly efficient in converting fuel or heat into electricity, resulting in lower fuel consumption and reduced greenhouse gas emissions per unit of electricity generated.
-
Scalability: These plants can be easily scaled up or down to meet varying electricity demand, making them adaptable to changing energy needs.
-
Energy Independence: In regions with abundant domestic fossil fuel resources, thermal power plants can enhance energy security by reducing reliance on imported energy sources.
-
Energy Storage Compatibility: Thermal power plants can be combined with energy storage solutions, such as thermal storage or battery systems, to improve grid stability and address intermittent renewable energy sources' variability.
Disadvantages of Thermal Power Plants:
-
Greenhouse Gas Emissions: The burning of fossil fuels in conventional thermal power plants releases carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change and air pollution. Additional, Thermal power fly ash is an environmental problem that requires in-depth research and a comprehensive solution.
-
Resource Depletion: The extraction and consumption of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, deplete finite resources and can lead to environmental degradation through mining, drilling, and transportation.
-
Water Consumption: Many thermal power plants require significant amounts of water for cooling purposes, potentially leading to water scarcity issues, especially in arid regions.
-
Environmental Impact: The discharge of heated water back into natural water bodies can harm aquatic ecosystems, and the release of air pollutants can have detrimental effects on local air quality and human health.
-
High Capital Costs: Building and maintaining thermal power plants can be expensive, and decommissioning old plants and managing their waste can also pose financial challenges.
Solutions to Mitigate Disadvantages:
-
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): Implementing CCS technology can capture CO2 emissions from thermal power plants, reducing their impact on the environment.
-
Fuel Switching: Transitioning from coal to natural gas or integrating renewable energy sources into thermal power plants can lower emissions and reliance on fossil fuels.
-
Advanced Cooling Technologies: Utilizing dry cooling or closed-loop cooling systems can reduce water consumption and minimize environmental impacts.
-
Improved Efficiency: Investing in advanced technologies and equipment can enhance the overall efficiency of thermal power plants, reducing fuel consumption and emissions.
-
Renewable Integration: Combining thermal power plants with renewable energy sources like solar and wind can provide more sustainable and flexible energy solutions.
-
Regulatory Measures: Governments can implement stricter environmental regulations, emissions standards, and incentives to encourage cleaner and more sustainable practices in the thermal power generation sector.
-
Collect thermal power fly ash right at the factory, ensuring the quality of the working environment and the health of people operating the factory.
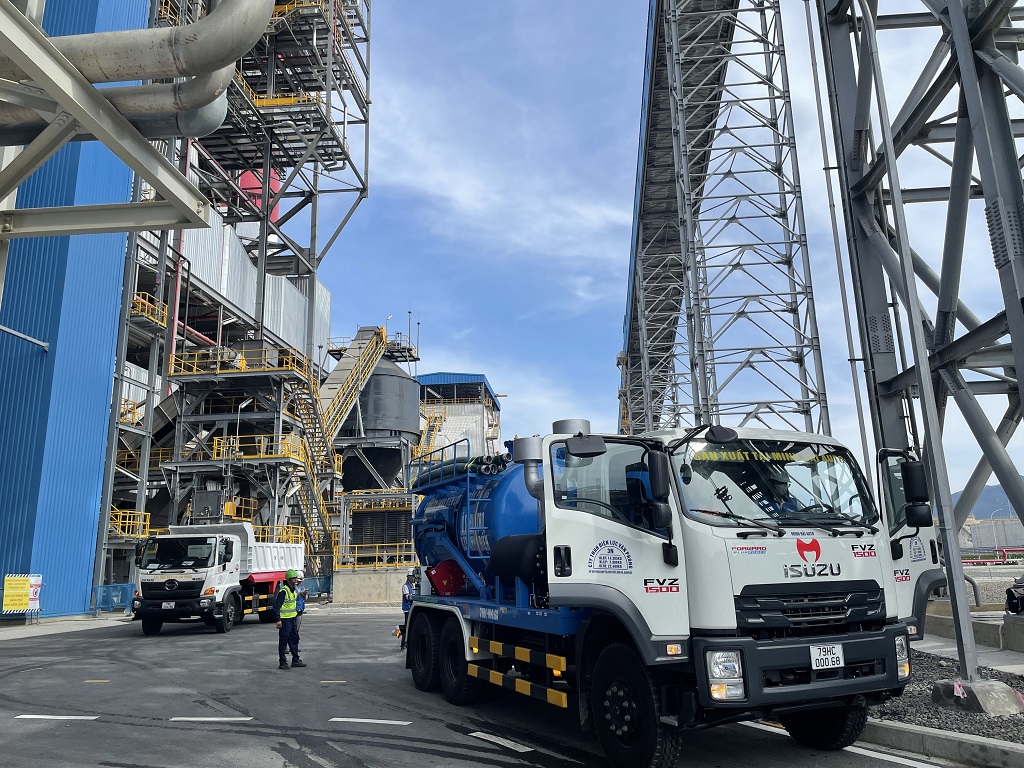

In conclusion, thermal power plants have both advantages and disadvantages, and their long-term sustainability depends on addressing the environmental and social challenges associated with their operation. Transitioning towards cleaner and more efficient technologies and integrating renewable energy sources can help mitigate the drawbacks of traditional thermal power generation.
